Constipation & Urine Issue and It's Solution
Posted By Intrinsic Training, Coaching, Seminar, Workshop HiiLSE GLOBAL VENTURES Corporate on 07/01/2021 3:54 AM
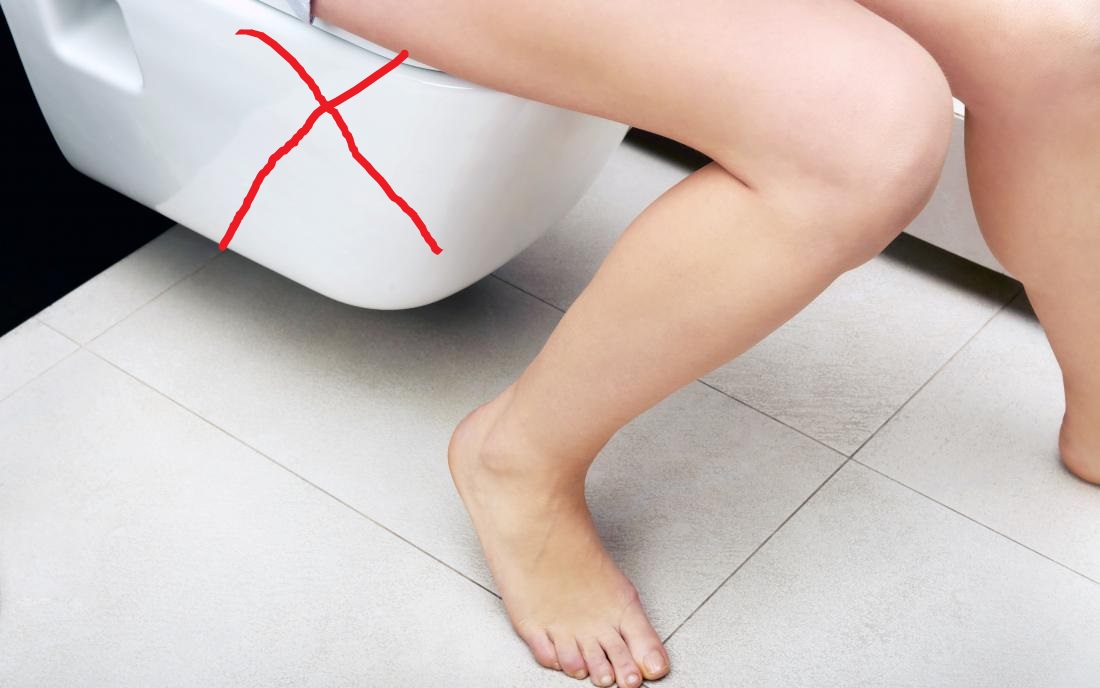
Constipation occurs when bowel movements become less frequent and stools become difficult to pass. It happens most often due to changes in diet or routine, or due to inadequate intake of fiber.
Buy Now! 35 Minutes Coaching
Experience Proven Methods
How naturally within a minute to push stools and urine out?
Easy to learn and Simple to apply posture!
Coupon Code 50% Discount
CORCi50p
Urinary retention is the inability to empty the bladder. Urinary retention can be acute or chronic. Acute urinary retention is a medical emergency.
Urinary retention is most common in men in their 50s and 60s because of prostate enlargement. A woman may experience urinary retention if her bladder sags or moves out of the normal position (cystocele) or pulled out of position by a sagging of the lower part of the colon (rectocele).
What is constipation?
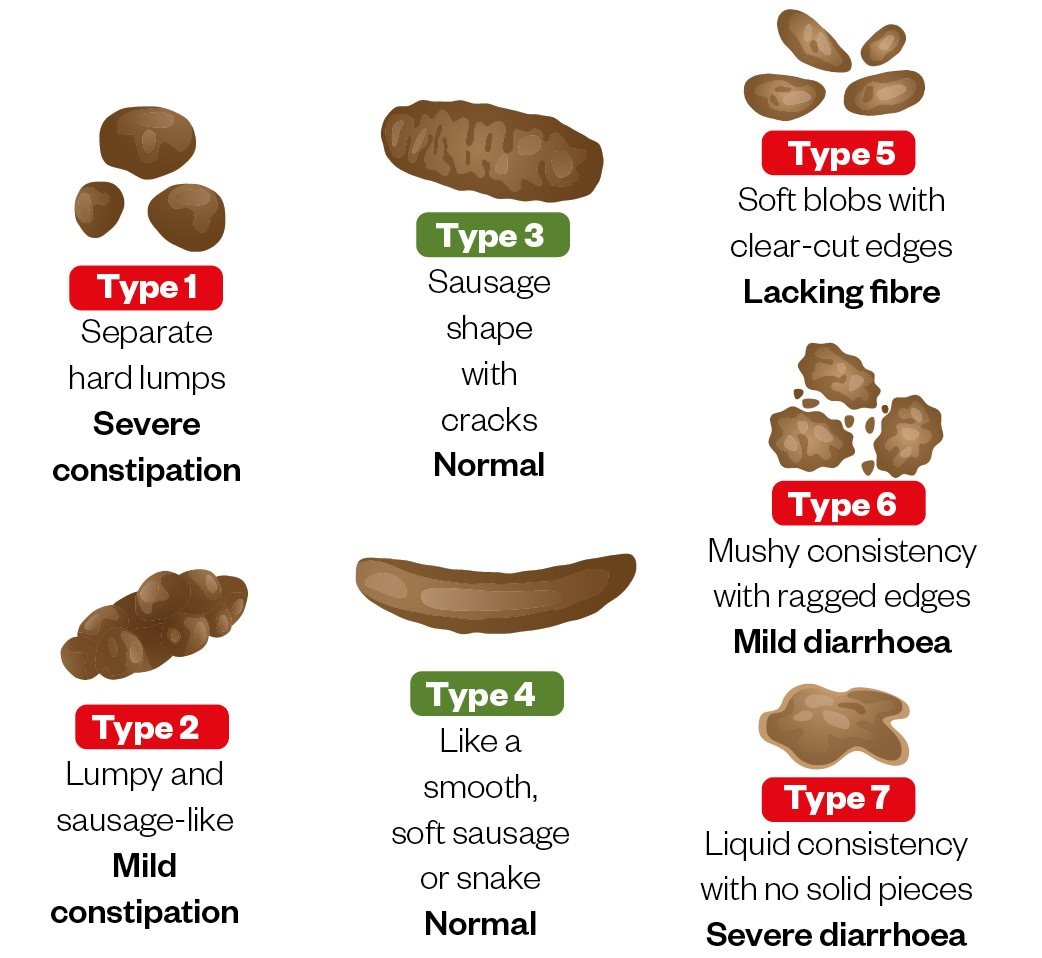
Having fewer than three bowel movements a week is, technically, the definition of constipation. However, how often you “go” varies widely from person to person. Some people have bowel movements several times a day while others have them only one to two times a week. Whatever your bowel movement pattern is, it’s unique and normal for you – as long as you don’t stray too far from your pattern.
Regardless of your bowel pattern, one fact is certain: the longer you go before you “go,” the more difficult it becomes for stool/poop to pass. Other key features that usually define constipation include:
- Your stools are dry and hard.
- Your bowel movement is painful and stools are difficult to pass.
- You have a feeling that you have not fully emptied your bowels.
How common is constipation?
You are not alone if you have constipation. Constipation is one of the most frequent gastrointestinal complaints in the United States. At least 2.5 million people see their doctor each year due to constipation.
People of all ages can have an occasional bout of constipation. There are also certain people and situations that are more likely to lead to becoming more consistently constipated (“chronic constipation”). These include:
- Older age. Older people tend to be less active, have a slower metabolism and less muscle contraction strength along their digestive tract than when they were younger.
- Being a woman, especially while you are pregnant and after childbirth. Changes in a woman’s hormones make them more prone to constipation. The baby inside the womb squishes the intestines, slowing down the passage of stool.
- Not eating enough high-fiber foods. High-fiber foods keep food moving through the digestive system.
- Taking certain medications (see causes).
- Having certain neurological (diseases of the brain and spinal cord) and digestive disorders (see causes).
How does constipation happen?
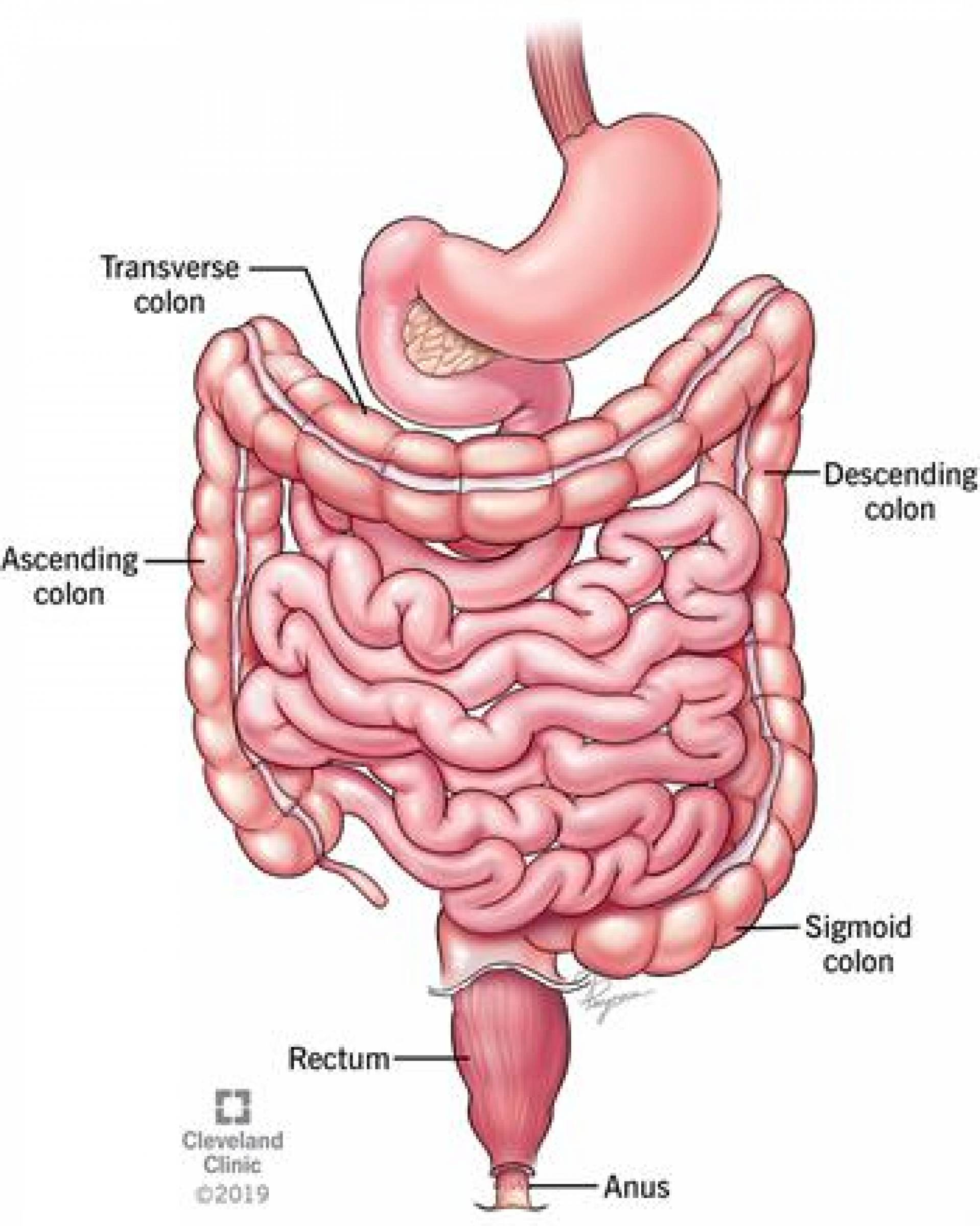
Constipation happens because your colon absorbs too much water from waste (stool/poop), which dries out the stool making it hard in consistency and difficult to push out of the body.
To back up a bit, as food normally moves through the digestive tract, nutrients are absorbed. The partially digested food (waste) that remains moves from the small intestine to the large intestine, also called the colon. The colon absorbs water from this waste, which creates a solid matter called stool. If you have constipation, food may move too slowly through the digestive tract. This gives the colon more time – too much time – to absorb water from the waste. The stool becomes dry, hard, and difficult to push out.
Can constipation cause internal damage or lead to other health problems?
There are a few complications that could happen if you don’t have soft, regular bowel movements. Some complications include:
- Swollen, inflamed veins in your rectum (a condition called hemorrhoids).
- Tears in the lining of your anus from hardened stool trying to pass through (called anal fissures).
- An infection in pouches that sometimes form off the colon wall from stool that has become trapped and infected (a condition called diverticulitis)
- A pile-up of too much stool/poop in the rectum and anus (a condition called fecal impaction).
- Damage to your pelvic floor muscles from straining to move your bowels. These muscles help control your bladder. Too much straining for too long a period of time may cause urine to leak from the bladder (a condition called stress urinary incontinence).
Does not having regular bowel movements cause toxins to build up in my body and make me sick?
Don’t worry, this usually isn’t the case. Although your colon holds on to stool longer when you are constipated and you may feel uncomfortable, the colon is an expandable container for your waste. There is possibly a slight risk of a bacterial infection if waste gets into an existing wound in the colon or rectum.
What causes constipation?
There are many causes of constipation – lifestyle choices, medications, medical conditions, and pregnancy.
Common lifestyle causes of constipation include:
- Eating foods low in fiber.
- Not drinking enough water (dehydration).
- Not getting enough exercise.
- Changes in your regular routine, such as traveling or eating or going to bed at different times.
- Eating large amounts of milk or cheese.
- Stress.
- Resisting the urge to have a bowel movement.
Medications that can cause constipation include:
- Strong pain medicines, like the narcotics containing codeine, oxycodone (Oxycontin®) and hydromorphone (Dilaudid®).
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, like ibuprofen (Advil®, Motrin®) and naproxen (Aleve®).
- Antidepressants, including the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (like fluoxetine [Prozac®]) or tricyclic antidepressants (like amitriptyline [Elavil®]).
- Antacids containing calcium or aluminum, such as Tums®.
- Iron pills.
- Allergy medications, such as antihistamines (like diphenhydramine [Benadryl®]).
- Certain blood pressure medicines, including calcium channel blockers (like verapamil [Calan SR], diltiazem [Cardizem®] and nifedipine [Procardia®]) and beta-blockers (like atenolol [Tenormin®]).
- Psychiatric medications, like clozapine (Clozaril®) and olanzapine (Zyprexa®).
- Anticonvulsant/seizure medications, such as phenytoin and gabapentin.
- Antinausea medications, like ondansetron (Zofran®).
Many drugs can cause constipation. Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you have any questions or concerns.
Medical and health conditions that can cause constipation include:
- Endocrine problems, like underactive thyroid gland (hypothyroidism), diabetes, uremia, hypercalcemia.
- Colorectal cancer.
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
- Diverticular disease.
- Outlet dysfunction constipation. (A defect in the coordination of pelvic floor muscles. These muscles support the organs within the pelvis and lower abdomen. They are needed to help release stool.)
- Neurologic disorders including spinal cord injury, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and stroke.
- Lazy bowel syndrome. The colon contracts poorly and retains stool.
- Intestinal obstruction.
- Structural defects in the digestive tract (like fistula, colonic atresia, volvulus, intussusception, imperforate anus, or malrotation.)
- Multiple organ diseases, such as amyloidosis, lupus, and scleroderma.
Pregnancy.
What are the symptoms of constipation?
Symptoms of constipation include:
- You have fewer than three bowel movements a week.
- Your stools are dry, hard and/or lumpy.
- Your stools are difficult or painful to pass.
- You have a stomach ache or cramps.
- You feel bloated and nauseous.
- You feel that you haven’t completely emptied your bowels after a movement.
Urinary retention and It's Solution
Causes of urinary retention include an obstruction in the urinary tract such as an enlarged prostate or bladder stones, infections that cause swelling or irritation, nerve problems that interfere with signals between the brain and the bladder, medications, constipation, urethral stricture, or a weak bladder muscle.
Symptoms of acute urinary retention are severe discomfort and pain, an urgent need to urinate but you simply can't, and bloated lower belly. Chronic urinary retention symptoms are mild but constant discomfort, difficulty starting a stream of urine, weak flow of urine, needing to go frequently, or feeling you still need to go after you've finished.
Complications include urinary tract infections (UTIs), bladder damage, and chronic kidney disease.
Tests to diagnose urinary retention include taking a urine sample, bladder scan, cystoscopy, X-ray and CT scan, blood test for prostate-specific antigen (PSA), prostate fluid sample test, and urodynamic tests to measure the bladder's ability to empty steadily and completely.
Treatment for urinary retention includes catheterization, treating prostate enlargement, and surgery.
Tags: constipation, colon cleaning, past motion, past urine